Federal Reserve’s 0.25 Percentage Point Interest Rate Increase to 5%
Synopsis
The Federal Reserve raised interest rates by 0.25 percentage points, bringing the target range for the federal funds rate from 4.75% to 5%. While this may have implications on borrowing costs and certain industries, the Fed is committed to achieving its goals of maximum employment and inflation at the rate of 2 percent over the longer run.
Investors with high-end assets should have a diversified portfolio that includes a mix of stocks, bonds, and other investments to weather any changes in the economic landscape. Seeking professional financial advice and maintaining a long-term perspective can help investors achieve their financial goals.

Federal Reserve Announces 0.25 Percentage Points Interest Rate Hike
In March 2023, the Federal Reserve made an announcement of a 0.25 percentage point interest rate hike in line with market expectations, raising the target range for the federal funds rate from 4.75% to 5%. The decision was made amid modest growth in spending and production, job gains, and elevated inflation. However, the Federal Reserve acknowledged that recent developments could lead to tighter credit conditions for households and businesses, with the current banking crisis potentially having negative impacts on the US economy, weighing on economic activity, hiring, and inflation.
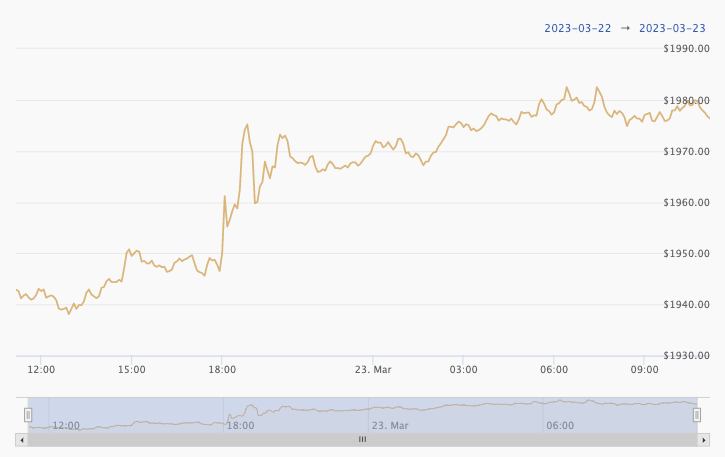
USD Gold Prices Increase After Fed Announcement
Implications of the Fed Rate Hike on the Economy
The Fed's decision to raise interest rates will have significant implications for the economy, particularly on borrowing costs. For businesses, a higher interest rate means it will cost more to borrow money to finance growth, making it more challenging to expand operations.
- The rise in interest rates is also likely to affect mortgage rates, making it more difficult for homebuyers to afford a new home. With fewer people being able to afford a home, it could potentially lead to a slowdown in the housing market.
- Additionally, the increase in interest rates may impact auto loans, as the cost of borrowing for a car increases as interest rates rise. This can make it more expensive for consumers to purchase a new car, which could lead to a slowdown in the auto industry.
- Furthermore, the Fed rate hike is also expected to affect stock market performance and investments such as bonds, mutual funds, and retirement accounts. When interest rates rise, it can make it more expensive for companies to borrow money to finance growth, which can lead to a decrease in stock prices. The impact of rising interest rates on the stock market may be short-term, but over the long-term, it is believed to lead to increased corporate earnings and higher stock prices.
The Fed's Commitment to Achieving Its Goals
It is crucial to note that the Fed's decision to raise interest rates is not necessarily negative. In fact, it can be a sign of a strong economy and a way to combat inflation. The Fed is committed to returning inflation to its 2 percent objective, and raising interest rates is one way to achieve this goal.
Although the rate hike may have short-term negative effects, such as higher borrowing costs and potential slowdowns in certain industries, it is important to consider the long-term benefits. By raising interest rates, the Fed is reducing the risk of inflation spiraling out of control, which can have serious negative impacts on the economy. The Fed is highly attentive to inflation risks and will continue to monitor incoming information and assess the implications for monetary policy. The Federal Reserve expects that implementing further policy measures may be necessary to achieve a monetary policy position that is adequately restrictive and will ultimately result in inflation returning to 2 percent.
When deciding on the degree of future target range increases, the Federal Reserve will consider the combined effects of previous monetary policy tightening, the time lags involved in the relationship between monetary policy, economic activity, and inflation, as well as economic and financial circumstances.
The Importance of Diversification for High-End Assets
For individuals with high-end assets, it is crucial to have a well-diversified portfolio that includes a mix of stocks, bonds, and other investments to weather any changes in the economic landscape. It is essential to maintain a long-term perspective and not be swayed by short-term fluctuations in the markets. By having a diversified portfolio, investors can reduce the risk of losing money during market downturns while still having the potential for long-term growth.
Investors and individuals should remain vigilant and informed, adjusting their strategies accordingly in response to any changes in the economic landscape. Despite the potential negative implications of the Fed rate hike, it is crucial to remember that the US economy has shown strong resilience in the face of challenges in recent years.
Furthermore, individuals with high-end assets should also consider seeking professional financial advice to help them navigate the complexities of the financial landscape. A financial advisor can provide guidance on developing an investment strategy that aligns with the investor's financial goals and risk tolerance. They can also offer advice on diversification and risk management strategies to help protect the investor's assets and minimize the impact of economic fluctuations.
The Future of US Monetary Policy
The Fed's decision to raise interest rates is just one of the many complex issues that impact the US economy. However, the Fed remains committed to achieving its goals of maximum employment and inflation at the rate of 2 percent over the longer run.
It is worth noting that the Fed's decision to raise interest rates may not be the end of the story. The Federal Reserve expects that implementing further policy measures may be necessary to achieve a monetary policy position that is adequately restrictive and will ultimately result in inflation returning to 2 percent. The Fed will continue to monitor economic and financial developments to determine the appropriate path for monetary policy.
Related Articles
This guide and its content is copyright of Chard (1964) Ltd - © Chard (1964) Ltd 2024. All rights reserved. Any redistribution or reproduction of part or all of the contents in any form is prohibited.
We are not financial advisers and we would always recommend that you consult with one prior to making any investment decision.
You can read more about copyright or our advice disclaimer on these links.